
Understanding GLP-1 Medications: Wegovy, Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Semaglutide
Over the past few decades more and more research has focused on understanding the complex factors contributing to obesity in order to find more effective solutions for this growing global epidemic. Scientists and healthcare professionals have been exploring not just the physical aspects of obesity, such as metabolism and hormonal regulation, but also the fat-from-stress/”>psychological, environmental, and genetic factors that play a role in weight gain. As a result, new treatments and medications are being developed, targeting different pathways in the body to help people manage their weight more effectively and improve their overall health. This has led to significant advancements in how we approach obesity, shifting from simple diet and exercise interventions to more holistic and personalized medical treatments.
What is a GLP-1 Medication?
GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, which is a hormone naturally produced by the intestines in response to eating. It plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of insulin (Figure 1) when blood sugar levels rise and by suppressing the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels.
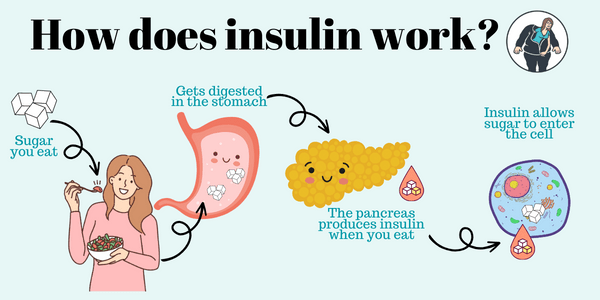
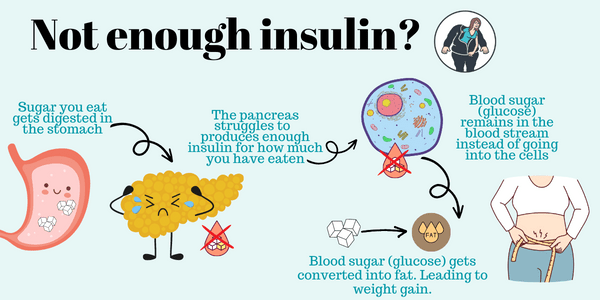
Additionally, GLP-1 slows down the emptying of the stomach, making people feel fuller longer, which can lead to a reduction in food intake. If we don’t have enough insulin, we tend to gain extra fat, among other health consequences.
GLP-1 receptor agonists are medications that mimic the action of this natural hormone. They bind to GLP-1 receptors in the pancreas, brain, and other parts of the body to help manage blood sugar levels and reduce appetite. These medications have become an important treatment option for people with type 2 diabetes and, more recently, for weight loss.
How Do GLP-1 Medications Work?
GLP-1 receptor agonists work by mimicking the effects of natural GLP-1 in the body. They primarily affect the pancreas, where they enhance the secretion of insulin, helping lower blood sugar after meals. At the same time, they reduce the production of glucagon, which helps prevent blood sugar levels from rising too high.
In addition to their effects on insulin and glucagon, GLP-1 medications influence the brain by activating receptors involved in appetite control. This results in a reduction in hunger, making these medications useful for weight loss as well.
Another benefit of GLP-1 medications is their ability to slow down gastric emptying (the rate at which food leaves the stomach). This not only helps regulate blood sugar spikes after meals but also promotes a sense of fullness, leading to reduced food intake over time.
Now, let’s dive into the individual drugs that fall under the GLP-1 receptor agonist category, including Wegovy, Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Semaglutide.

If you’re struggling with managing your weight, it’s important to remember that you’re not alone, and seeking professional support can make all the difference. obesity is a complex condition that often requires more than just diet and exercise to effectively address. At MD diet clinic, our experienced medical providers specialize in weight loss and can offer personalized treatment plans tailored to your needs. Whether you’re considering medications like Wegovy, Ozempic, or other options, our team is here to help guide you through the process safely and effectively. Don’t hesitate to take the next step toward better health—call today to explore the best strategies for your weight loss journey.
Salt Lake clinic: 801-758-2130
Wegovy, Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Semaglutide: A Detailed Comparison
1. Wegovy (Semaglutide)
- Indication: Primarily used for weight management in individuals with obesity or overweight with at least one weight-related condition, such as high blood pressure or type 2 diabetes.
- Dosage Form: Wegovy is administered as a once-weekly subcutaneous injection.
- Mechanism of Action: Wegovy is a higher-dose version of semaglutide specifically developed for weight loss. It mimics the GLP-1 hormone to suppress appetite, reduce food intake, and enhance satiety. In clinical trials, Wegovy has shown significant results in helping people lose 15-20% of their body weight when combined with lifestyle changes.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, and potential gallbladder issues.
Wegovy is best suited for patients focused on substantial weight loss rather than solely managing blood sugar levels. It is not a diabetes treatment but a weight management medication, making it distinct from other semaglutide-based drugs like Ozempic.
2. Ozempic (Semaglutide)
- Indication: Ozempic is primarily used for treating type 2 diabetes by improving blood sugar control. It can also help with weight loss as a secondary benefit.
- Dosage Form: Ozempic is also administered as a once-weekly injection, but in a lower dose compared to Wegovy.
- Mechanism of Action: As a GLP-1 receptor agonist, Ozempic works similarly to Wegovy by mimicking the GLP-1 hormone. It enhances insulin production, reduces glucagon release, and slows gastric emptying. While not marketed solely as a weight loss drug, some patients experience weight loss as a result of its action on appetite regulation.
- Side Effects: Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and constipation are common, with more serious side effects including pancreatitis and potential thyroid tumors in rare cases.
Ozempic is often prescribed for people with type 2 diabetes who also want to lose some weight. Though it shares the same active ingredient (semaglutide) as Wegovy, it is used primarily for glycemic control, with weight loss as an additional benefit rather than the main focus.
3. Mounjaro (Tirzepatide)
- Indication: Mounjaro is a newer drug approved for type 2 diabetes management. It has shown promising results in weight loss, though it is not yet officially approved for this use.
- Dosage Form: Mounjaro is administered as a weekly subcutaneous injection.
- Mechanism of Action: Mounjaro is unique in that it targets two different hormone pathways: GLP-1 and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). This dual mechanism enhances its ability to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood sugar levels, and promote weight loss. Studies have shown that Mounjaro may lead to greater weight loss compared to semaglutide, making it a powerful option for individuals looking for both blood sugar control and significant weight loss.
- Side Effects: Like other GLP-1 medications, Mounjaro’s side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It may also carry risks of pancreatitis and thyroid tumors.
Mounjaro’s dual mechanism may make it more effective for weight loss compared to other GLP-1 receptor agonists, though its current approval is limited to type 2 diabetes management.
4. Semaglutide
- Indication: Semaglutide is the active ingredient in both Wegovy and Ozempic, but it can also be prescribed under its own name as a medication for type 2 diabetes. In lower doses, it works to regulate blood sugar levels, while in higher doses (such as in Wegovy), it becomes a weight loss aid.
- Dosage Form: Like the branded versions, semaglutide is available as a weekly injection.
- Mechanism of Action: The action of semaglutide mirrors that of natural GLP-1 by regulating blood sugar, enhancing insulin production, and reducing food intake by slowing gastric emptying.
- Side Effects: Nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal issues are common, as well as a risk of thyroid tumors in some cases.
Semaglutide can be used as a generic treatment for diabetes or weight loss, depending on the dose prescribed.
Key Differences Between Wegovy, Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Semaglutide
Now that we’ve covered the basics of each drug, let’s summarize their differences in the following table:
| Drug | Active Ingredient | Indication | Dose Form | Primary Use | weight loss Effect | Side Effects |
|---|
| Wegovy | Semaglutide | obesity/weight management | Weekly subcutaneous injection | weight loss | High | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, potential gallbladder issues |
| Ozempic | Semaglutide | Type 2 diabetes | Weekly subcutaneous injection | Blood sugar control | Moderate | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, risk of pancreatitis |
| Mounjaro | Tirzepatide | Type 2 diabetes | Weekly subcutaneous injection | Blood sugar control | High (off-label use) | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, risk of thyroid tumors |
| Semaglutide | Semaglutide | Type 2 diabetes/weight loss | Weekly subcutaneous injection | Blood sugar/weight loss | Moderate to High | Similar to branded semaglutide (nausea, vomiting, GI issues) |
Conclusion
GLP-1 receptor agonists have revolutionized the treatment landscape for both type 2 diabetes and weight management.
Wegovy, Ozempic, Mounjaro, and Semaglutide all work by mimicking the body’s natural GLP-1 hormone, helping regulate blood sugar and reduce appetite. Wegovy stands out for its high-dose formulation specifically for weight loss, while Ozempic focuses primarily on managing blood sugar with weight loss as a secondary benefit. Mounjaro, with its dual-target mechanism, shows exceptional promise for weight loss and blood sugar control, though it’s currently approved only for diabetes management.
Understanding the differences between these drugs allows healthcare providers to tailor treatments based on individual patient needs, balancing blood sugar management and weight loss goals.



